Understanding ABC Classification of Inventory for Maintenance Spare Parts
Examples from HVAC, Thermal Power Plants, Aviation and Oil & Gas Industries
Affiliate Disclosure: Handy Tool Adviser is reader-supported. When you buy through links on our site, we may earn an affiliate commission at no cost to you. Read more about our affiliate association here.
If you’ve been working in maintenance department of any industry, you might have heard the term ABC classification of inventory. Our purpose in this article is to explain in a practical way (with examples) about how ABC classification of inventory works on maintenance spare parts.
Our focus will be to first explain the concept of ABC classification with emphasis on maintenance spare parts and then give examples from different industries to ensure better understanding of the topic.
How ABC Classification is the Natural Classification of Spare Parts
The first thing to understand about the ABC classification of MRO inventory is that it is not like the categories were made first and then items were put into those categories. It is as if the categories were discovered.
What is that supposed to mean?
In any maintenance facility, there are some parts and materials that are used frequently while some that are not used frequently. It is not like the runner of a Francis turbine in a hydel power plant fails as often as a 16-ampere circuit breaker installed in plant’s switchgear.

A Francis Turbine Runner
Hydel Power Plants around the world use a type of turbine known as Francis turbine. At the heart of Francis turbine is what is called a “runner”. It is a giant impeller-like part of the turbine (Image Credit: Wikimedia Commons)
What is another statistical fact is that the parts that are used rarely are generally the parts that are quite expensive. The runner of the Francis turbine will cost several thousand USD while the 16-ampere circuit breaker will cost USD 10-20.
The above two statistical commonalities form the two ends of the spectrum of ABC inventory classification.
Category-A inventory comprises parts that are rarely used and are very expensive like the runner of a Francis turbine mentioned above.
Category-C inventory comprises parts that are frequently used and are not expensive like the 10-ampere circuit breaker installed in plant’s switchgear.
Between these two ends of the spectrum is Category-B inventory i.e., the inventory falling in between the rarely used expensive parts and the frequently used inexpensive parts.
An example for the Category-B inventory is a ball bearing of a pump in the same power plant. It may need replacement after 5 years and cost a thousand dollars. Therefore, it falls between the Francis turbine runner and the
Let us expand on this ABC inventory classification by giving examples from different industries.
Examples of ABC Inventory Spare Parts in HVAC Industry
Let us first present some examples of Category-ABC inventory spare parts in HVAC industry i.e., Heating, Ventilation & Airconditioning Industry.
Category-A Inventory Spare Parts in HVAC
- Compressor motors
- Control boards for chillers
- Air handling unit (AHU) fan motors
- Heat exchangers for boilers
- Evaporator coils for air conditioning units
Category-B Inventory Spare Parts in HVAC
- Belts for fan drives
- Thermostats
- Expansion valves for refrigeration systems
- Pressure switches for HVAC systems
- Blower wheels for furnaces
Category-C Inventory Spare Parts in HVAC
- Filters for air conditioning units
- Gaskets for HVAC system components
- Screws and bolts for assembly of HVAC units
- Fuses for electrical panels
- Capacitors for HVAC motors
Examples of ABC Inventory Spare Parts in Thermal Power Plants
Now let us give some examples from thermal power plants.
Category-A Inventory Spare Parts in Thermal Power Plants
- Turbine blades
- Boiler tubes
- Generator stators and rotors
- Control valves for steam and water systems
- Exciters for generator systems
Category-B Inventory Spare Parts in Thermal Power Plants
- Bearings for turbine and generator systems
- Heat exchangers for feedwater systems
- Couplings for pumps and motors
- Igniters for boiler startup
- Instrumentation and control systems for plant automation
Category-C Inventory Spare Parts in Thermal Power Plants
- Lubrication oil filters
- Nozzles for fuel oil and gas systems
- Safety valves for steam and water systems
- Gaskets for pipe flanges and equipment connections
- Bearings for fans and blowers
Examples of ABC Inventory Spare Parts in Aviation Industry
Now, let us give examples of ABC inventory spare parts in Aircraft Maintenance.
Category-A Inventory Spare Parts in Aviation Industry
- Jet engine fan blades
- Landing gear components
- Avionics systems (such as flight management computers)
- Hydraulic system pumps and actuators
- Flight control surfaces (such as wings or flaps)
Category-B Inventory Spare Parts in Aviation Industry
- Airframe bolts and fasteners
- Tires and wheels
- Emergency equipment (such as life rafts or oxygen masks)
- Fuel pumps and filters
- Electrical connectors and wiring
Category-C Inventory Spare Parts in Aviation Industry
- Light bulbs and lamps
- Drain valves and gaskets
- Circuit breakers and fuses
- Oxygen sensors and filters
- Cabin interior components (such as seat covers or carpeting)
Examples of ABC Inventory Spare Parts in Oil & Gas Industry
Now, let us give examples of ABC inventory spare parts in Oil and Gas industry.
Category-A Inventory Spare Parts in Oil & Gas Industry
- Oil rig blowout preventers
- Drill bits and drill pipe
- Gas turbines and compressors
- Control valves for process control systems
- Subsea production equipment (such as subsea trees)
Category-B Inventory Spare Parts in Oil & Gas Industry
- Motors and pumps for wellheads and pipelines
- Electrical submersible pumps
- Chemical injection systems and pumps
- Control panels and switchgear
- Piping and tubing connectors and fittings
Category-C Inventory Spare Parts in Oil & Gas Industry
- Filters for oil and gas separation and processing
- Gaskets and seals for pipeline connections
- Gauges and pressure sensors
- Bolts, nuts, and washers for flanges and fittings
- O-rings and other small mechanical components
Examples of ABC Inventory Spare Parts in Water Treatment Plant
Now, let us give examples of ABC inventory spare parts in Water Treatment Plant.
Category-A Inventory Spare Parts in Water Treatment Plant
- Large water pumps and motors
- High-capacity clarifiers and filters
- Ultraviolet disinfection systems
- Reverse osmosis membranes
- Large-scale chemical feed systems
Category-B Inventory Spare Parts in Water Treatment Plant
- Membrane cleaning chemicals and equipment
- Valves and actuators for flow control
- Electric motors and variable frequency drives
- Blowers and aerators for aeration tanks
- pH sensors and control systems
Category-C Inventory Spare Parts in Water Treatment Plant
- Filter cartridges and bags
- Chemical dosing pumps and tubing
- Air diffusers for aeration tanks
- UV bulbs and quartz sleeves
- Gaskets and seals for pumps and valves.
So, that is it from our side.
We hope you found our explanation and examples helpful. If yes, do share our work with someone likeminded.
Other Articles You May Like

brizy_dc_post_title
Learn about Autonomous Maintenance - part of Total Productive Maintenance that empowers machine operators in basic maintenance tasks.

brizy_dc_post_title
Learn what is RAMS - acronym of Reliability, Availability, Maintainability & Safety/Supportability - in industrial maintenance.

brizy_dc_post_title
We explain what is the supposed role of Maintenance Planning Department in industry. We clear misconceptions and give do's and don'ts.

brizy_dc_post_title
Explaining 6 industrial maintenance types: Preventive, Reactive, Corrective, Predictive, Proactive and Reliability Centered Maintenance.
brizy_dc_post_title
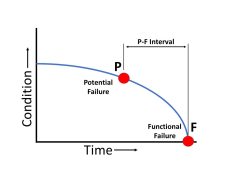
Practical aspects of PF Curve and PF Interval in maintenance & reliability explained. Learn what's the most important question in PF interval?

brizy_dc_post_title
The practical application of ABC classification of inventory for maintenance spare parts with examples from different industries.

brizy_dc_post_title
We explain the concept of Inherent Reliability - A metric used in industrial maintenance and reliability management.
brizy_dc_post_title
Intuitive explanation of Achieved Availability - Metric used in Industrial Maintenance & Reliability Management.
brizy_dc_post_title
Explaining in simple English the term Mean Time To Repair or Replace (MTTR) used in maintenance management.

brizy_dc_post_title
We explain the terms Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF) and Mean Time To Failure (MTTF) in simple and practical language.

brizy_dc_post_title
We give a detailed example of calculating Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) for HVAC equipment (in a story telling style).

brizy_dc_post_title
Explaining the 8 wastes of lean manufacturing (or lean production) philosophy that are applicable on maintenance management.

brizy_dc_post_title
Intuitive explanation of the difference between Total Effective Equipment Performance (TEEP) & Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE).

brizy_dc_post_title
We explain in layman terms what is Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) - a metric maintenance teams aim to maximize in industry.

brizy_dc_post_title
We explain a useful metric that is used by maintenance managers to determine efficiency of their maintenance workforce.

brizy_dc_post_title
We explain the maintenance work order system (or work management system) used by maintenance departments in simple words.