What is Achieved Availability in Maintenance & Reliability?
Intuitive Explanation with Example Calculation
Availability is a commonly used metric in engineering companies and manufacturing industry. It is a metric that captures the historical breakdowns and downtimes experienced in equipment while at the same time acts as a measure of probability of whether the machine will remain up in future.
So, for example, if we say that a hydraulic press has an availability of 90%, it means that historically, the machine remained available when needed 90% of the time. It also means that the hydraulic press is likely to remain available 90% of the time in future.
However, there different types of availability and it is important to understand which particular type gives us what we need. These types include:
- Achieved Availability
- Operational Availability
- Average Availability (or Mean Availability)
- Equipment Availability
- Inherent Availability
- Limiting Availability
- Point Availability (or Instantaneous Availability)
In today’s article, we will explain Achieved Availability in detail in an intuitive way. We will break down its formula to read between the lines of its mathematical expression to discover why is it given the name “Achieved” availability.
Understand the Mathematical Aspect
Achieved availability is calculated using the following mathematical expression:
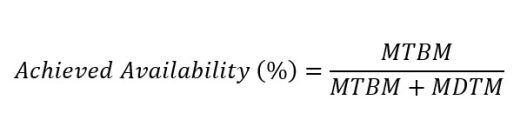
Where,
MTBM = Mean Time Between Maintenances
MDTM = Mean Downtime for Maintenance
When Will Achieved Availability (%) be High?
Instead of giving a bland descriptive explanation of above formula, let us simply ask:
When will Achieved Availability (%) give a high and desirable value?
Achieved Availability (%) will give a great value if:
- Mean Time Between Maintenances (MTBM) is large. When will MTBM be large? – When a machine doesn’t need to be checked again and again frequently or it doesn’t give faults frequently that call for corrective maintenance. The more a machine is ‘maintenance-free’ or has been made ‘fault-free’ by good work of maintenance team, the larger the MTBM.
- Mean Downtime for Maintenance (MDTM) is small. When will MDTM be small? – When the maintenance team doesn’t need to take the machine out of operation for long periods i.e., when maintenance is quickly completed and machine is given back in operation in minimum time.
So, based on above two factors, when will Achieved Availability (%) be great?
It will be great when the maintenance department keeps the machine in a highly reliable state such that it doesn’t call for maintenances frequently and whatever maintenance is performed, it is completed quickly without the need for taking the machine out of operation for an extended period of time.
When Will Achieved Availability (%) be Low?
The next natural question becomes that what will result in a low value for Achieved Availability?
It is simple. The same two factors that gave a high value will cause a low value when inverted.
How? – let us explain.
- Mean Time Between Maintenances (MTBM) is small. When will MTBM be small? – When a machine keeps giving faults frequently calling the maintenance team to do corrective or preventive maintenance on it again and again. The more a machine is unreliable in its operation, the more it will keep calling maintenance technician to fix it and the smaller the MTBM.
- Mean Downtime for Maintenance (MDTM) is large. When will MDTM be large? – When the maintenance team takes the machine out of operation for extended periods of time i.e., the maintenance interventions are lengthy and time consuming.
So, based on above two factors, when will Achieved Availability (%) be poor?
It will be poor when the machine keeps breaking down (or produces frequent faults) calling the maintenance team again and again to fix it and the maintenance over it takes too much time thereby causing the machine to remain out of operation for longer periods.
Example Calculation of Achieved Availability
Let’s say a robotic welder in Tesla’s gigafactory works 24/7 in the Tesla Model 3 production line. Tesla’s maintenance and reliability department is responsible for maintaining high uptime of the robotic welder.
Preventive Maintenance (PM) schedule of the robotic welder makes its inspection necessary every 6 months and the complete PM checklist is completed in 1 hour.
In the year 2022, the robotic welder experienced unforeseen faults 10 times due to which production was affected and maintenance team had to rush a technician to fix it. Some faults took an hour to fix while others took several minutes. Record showed an averaged out corrective maintenance time of 1 hour for the said fault rectifications.
We want to calculate the Achieved Availability (%) of the above-mentioned robotic welder for the year 2022. It is expressed as:
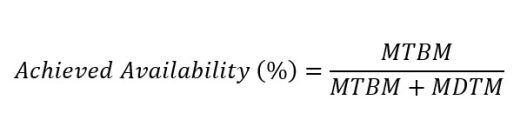
Therefore, we will first calculate its components one by one.
Calculating Mean Time Between Maintenances (MTBM)
The first thing we have to calculate is the Mean Time Between Maintenances (MTBM) for the year 2022.
The six-monthly PM was performed twice in one year while corrective maintenance was performed ten times in one year making the total maintenances performed as twelve (12) in one year.

Calculating Mean Downtime of Maintenances (MDTM)
Next, we need to calculate the Mean Downtime of Maintenance (MDTM). It is calculated as under:
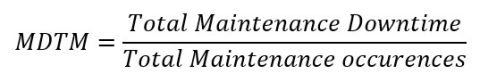
Where,
Total Maintenance Downtime = (1-hour/PM x 2 Preventive Maintenances) + (1 hour/repair x 10 repair jobs) = 12 hours
And,
Total Maintenance Occurrences = 2 Preventive Maintenances + 10 Corrective Maintenances = 12 maintenance in total
Now, MDTM can be easily calculated for the year as under:

Calculating Achieved Availability
We have calculated the ingredients of Achieved Availability as under:
Mean Time Between Maintenances (MTBM) = 720 hours
Mean Downtime Between Maintenances (MDTM) = 1 hour
Now, we can finally calculate Achieved Availability:

Therefore, the loss in Achieved Availability has been 0.14%. The next target Tesla’s maintenance and reliability department could set for itself could be 99.99%.
In this way, Tesla’s maintenance and reliability department could calculate Achieved Availability (%) again next year to track improvement in the reliability of the robotic welder.
Conclusion
Achieved Availability is a metric used to measure the probability of a machine remaining operational in the future, based on historical breakdowns and downtimes. It is calculated using Mean Time Between Maintenances (MTBM) and Mean Downtime for Maintenance (MDTM).
Achieved Availability will be high when the MTBM is large and the MDTM is small, and low when these values are inverted. The name "Achieved" refers to the achievement of the maintenance and reliability department in improving the reliability of the equipment, leading to a higher availability.
If you liked this article, please do share it with at least one like-minded person.
If you liked this post, please share it with someone who may benefit from it.
Other article suggestions